Causes of Hair Loss
in Men
 Hair loss or baldness is a genetic trait—but unlike what you may have been told, it’s not necessarily passed down from your maternal grandfather. Medical science has come to learn that baldness genes are actually passed down from both sides of the family—and they affect hair loss in women as well as men. Baldness genes may also skip generations and are utterly random in terms of which siblings (male or female) they will affect. They may even have very different effects on siblings in the same family.
Hair loss or baldness is a genetic trait—but unlike what you may have been told, it’s not necessarily passed down from your maternal grandfather. Medical science has come to learn that baldness genes are actually passed down from both sides of the family—and they affect hair loss in women as well as men. Baldness genes may also skip generations and are utterly random in terms of which siblings (male or female) they will affect. They may even have very different effects on siblings in the same family.
Hair loss in men
Androgenetic Alopecia, or “male pattern baldness,” occurs in men whose hair follicles are sensitive to the hormone dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. Over time, DHT-sensitive hair (usually found on the top and front of the head) becomes weaker, finer, and eventually stops growing. However, even men who experience advanced baldness have healthy hair follicles around the sides of the head that last a lifetime. Even though these healthy hairs are exposed to DHT, they are resistant to this hormone and survive for a lifetime.
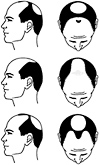
Male Baldness: The Norwood Scale
Class 1
Represents a normal head of hair with no visible hair loss.Class 2
Characterized by the beginning of a receding hairline and a “widow’s peak” on the forehead.Class 3
Patients exhibit a more significant decline in hair above the temples as well as receding from the forehead. In Class 3 Vertex, hair loss is starting to become significant on the crown.Class 4
Hair loss may become more noticeable on the crown or patients may have significant hair loss above the temples and/or front anterior areas.Class 5
Hair loss approaches significant levels with most hair loss occurring on the top of the vertex and crown. Hair transplantation for this Class and higher Class levels may require more grafts to provide coverage and density.Class 6
Patients show major hair loss, but still have areas with donor hair available. Transplanting this hair can still have excellent results.Class 7
Patients show the most significant loss of hair. There may still be sufficient donor hair for transplantation; however, results may be limited.
This chart illustrates the stages used by medical professionals when discussing the progression of male pattern hair loss (MPHL). You may find it useful in helping determine your stage. The chart divides the pattern of male hair loss into 7 categories.

Hair Restoration options
While surgical hair transplantation is the only permanent and the most significant solution to hair loss, these other solutions can help in your fight against hair loss.
* Surgical Hair Transplantation
* LRHT (Laser-Revivogen-Hair Treatment)
* TLHT (Tricomax-Laser-Hair Treatment)
* Non- Surgical Hair Replacement
Surgical hair transplantation
Surgical hair transplantation involves transplanting hairs and follicles from one area of the head to another. Most causes of hair moss may be traced to the hormone DHT. In hair transplantation, DHT-resistant follicles are removed from the scalp and artfully placed in thinning areas on the top and front of the head. Our patients find there are many benefits of hair transplantation over other treatment options
Hair transplantation is widely considered to be the most effective option for restoring hair because it’s a permanent, relatively simple procedure, and it achieves a natural look.
A permanent solution
Hair transplantation is permanent. Because the transplanted hairs are already resistant to the DHT hormone that causes hair loss, they will not thin or fall out in the future. Depending on your hair loss classification and stage of hair loss, our physician may recommend the use of the LRHT or TLHT to help maintain non-DHT resistant hairs and prevent future thinning.
Vivandi Trading LLC
Gulf Towers, Tower B2, Suite 404
Oud Metha Road, Dubai, UAE

